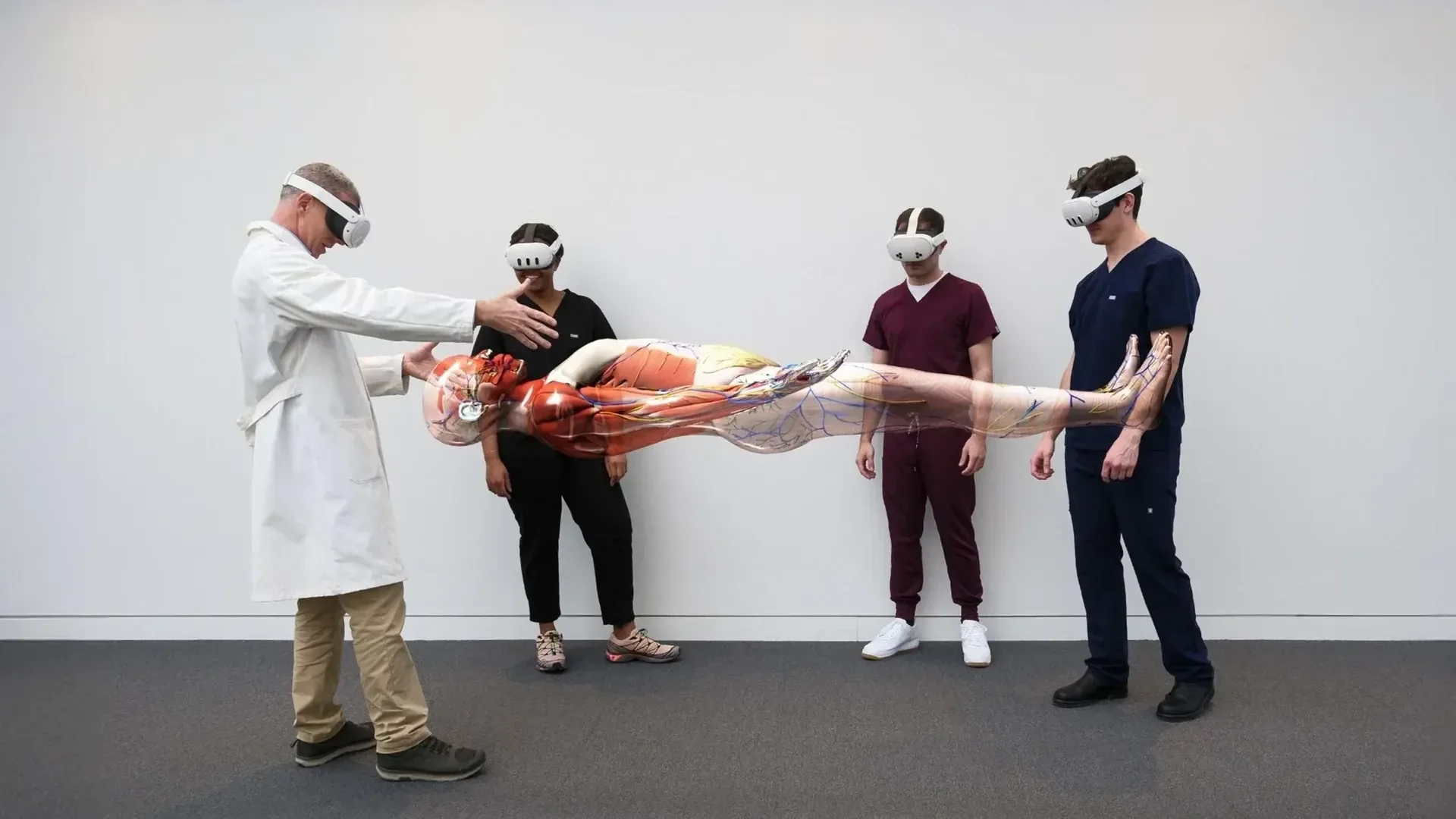
HoloAnatomy® Research Findings
Preliminary studies on HoloAnatomy® suggest gains in efficiency, retention, and engagement. Across multiple peer-reviewed and partner studies, students learning with mixed-reality reported stronger comprehension, higher engagement, and equal or better assessment outcomes compared to traditional cadaver-only methods.
This page provides summaries of key findings with direct links to original research.
Key Findings at a Glance
Reduced study time by up to one-third without sacrificing learning outcomes.
Retention increased by up to 40% compared to dissection-only cohorts.
Boosted engagement across behavioral, emotional, and cognitive dimensions.
Stronger comprehension and confidence when supplementing dissection
Study Summaries
Transforming Anatomy Education with Mixed Reality
At Jagiellonian University, 97% of first-year medical students reported improved anatomical understanding and 90% felt better prepared for dissection labs after using HoloAnatomy®
Mixed-Reality as a Supplement to Cadaveric Dissection
Students learning breast anatomy with HoloAnatomy retained information 40% better eight months later and reported MR was easier for teamwork.
👉 Comparing learning retention in medical students using mixed-reality to supplement dissection
Remote Anatomy Education with Mixed Reality
84% of students believed anatomy can be effectively learned remotely via MR, with 81% citing advantages like flexibility and study space.
👉 Assessment of Mixed-Reality Technology Use in Remote Online Anatomy Education
Time Efficiency vs. Cadaveric Dissection
Students required ~4.6 hours with HoloAnatomy vs. 7.3 hours (1/3 less) in cadaver lab, achieving similar exam results.
👉 Mixed reality as a time-efficient alternative to cadaveric dissection
Comparative Effectiveness Study
Exam scores were statistically equivalent between MR and cadaver groups, validating HoloAnatomy as an effective alternative.
Student Engagement
Mixed reality increased engagement (curiosity, participation, responsiveness) and reduced signs of disengagement compared to traditional methods.
While these studies suggest meaningful benefits of mixed-reality in anatomy education, most were conducted with limited sample sizes and within specific curricular contexts. Results may vary by institution, content area, and implementation.
From Research to Practice
The studies above show how mixed-reality anatomy learning can reduce study time, improve retention, and boost engagement. HoloAnatomy® .NEXT™ brings these benefits to today’s classrooms with an immersive platform built for faculty and students.
Ready to see how HoloAnatomy® .NEXT™ could fit into your curriculum and extend these research findings into your own programs?